Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics
Click2Drug
Directory of computer-aided Drug Design tools
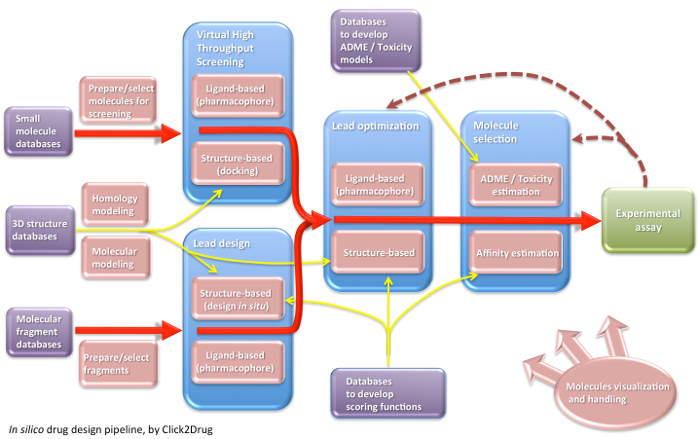
Click2Drug contains a comprehensive list of computer-aided drug design (CADD) software, databases and web services. These tools are classified according to their application field, trying to cover the whole drug design pipeline. If you think that an interesting tool is missing in this list, please contact usClick on the following picture to select tools related to a given activity:
Show all links Hide all links
Docking
Web services
- idTarget. Web server for identifying biomolecular targets of small chemical molecules with robust scoring functions and a divide-and-conquer docking approach. Maintained by the National Taiwan University.
Screening
Software
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.
Target prediction
Software
- PatchSearch. PatchSearch implements local searching for similar binding sites on protein surfaces with a controlled amount of flexibility. It is based on product graphs to represent all possible matchings between two structures. Developed and provided as an R package by Univeristé Paris-Diderot, France.
- MolScore-Antivirals. Expert system to identify and prioritise antiviral drug candidates. Developed by PharmaInformatic, Germany.
- MolScore-Antibiotics. Expert system to identify and prioritise antibacterial drug candidates. Developed by PharmaInformatic, Germany.
Web services
- SwissTargetPrediction. Online tool to predict the targets of bioactive small molecules in human and other vertebrates. This is useful to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying a given phenotype or bioactivity, to rationalize possible side-effects or to predict off-targets of known molecules. Provided by the Molecular Modeling group of the Swiss Institute of BioInformatics.
- SEA. SEA (Similarity ensemble approach) relates proteins based on the set-wise chemical similarity among their ligands. It can be used to rapidly search large compound databases, build cross-target similarity maps and predict possible targets of a small molecule. Provided by the Shoichet Laboratory in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
- CSNAP. CSNAP (Chemical Similarity Network Analysis Pull-down) is a computational approach for compound target identification based on network similarity graphs. Query and reference compounds are populated on the network connectivity map and a graph-based neighbor counting method is applied to rank the consensus targets among the neighborhood of each query ligand. Developed in the Torres lab at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
- ChemProt. The ChemProt 2.0 server is a ressource of annotated and predicted chemical-protein interactions. The server is a compilation of over 1 100 000 unique chemicals with biological activity for more than 15000 proteins. ChemProt can assist in the in silico evaluation of small molecules (drugs, environmental chemicals and natural products) with the integration of molecular, cellular and disease-associated proteins complexes. Provided by the Technical University of Denmark, and the University Paris Diderot.
- SuperPred. Webservice for drug classification and target prediction. The web-server translates a user-defined molecule into a structural fingerprint that is compared to about 6300 drugs, which are enriched by 7300 links to molecular targets of the drugs, derived through text mining followed by manual curation. Provided by the Institute of Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics, Charité - University Medicine Berlin.
- PASSonline. (Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances). Web service for evaluating the general biological potential of an organic drug-like molecule, based on the comparison of the user's compound to a database of 260,000 of drug-like biologically active compounds using the Multilevel Neighborhoods of Atoms (MNA) structure descriptors. Provided by the Orekhovich Institute of Biomedical Chemistry
- Target Hunter of Small Molecule. Web portal for predicting the therapeutic potential of small organic molecules based on chemogenomic database. Created and maintained by Prof. Xiang-Qun (Sean) Xie’s laboratory
- HitPick. Web server that facilitates the analysis of chemical screenings by identifing hits and predicting their molecular targets. For target prediction, HitPick applies an approach that combines two 2D molecular similarity based methods: a simple 1-Nearest-Neighbour similarity searching and a machine learning method based on Laplacian-modified naive Bayesian models. provided by the Helmholtz Center Munich, germany.
- Molinspiration bioactivity score. Score a compound for its ability to be GPCR ligand, ion channel modulator, kinase inhibitor, nuclear receptor ligand, protease inhibitor, enzyme inhibitor. Based on Bayesian statistics to compare structures of representative ligands active on the particular target with structures of inactive molecules and to identify substructure features (which in turn determine physicochemical properties) typical for active molecules. Provided by Molinspiration.
- ElectroShape Polypharmacology server. Web service to estimate polypharmacology profiles and side effects of compounds based on the molecular similarity concept. Developed and maintained by Alvaro Cortes Cabrera.
Ligand design
Software
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.
- ACD/Structure Design Suite. Helps chemists optimize the physicochemical properties of their compounds. The software suggests alternative substituents (at a site/sites on the molecule) to drive the property of choice in the desired direction. Helps adjust aqueous solubility, lipophilicity (logP or logD), or change the ionization profile (pKa) of molecules. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
QSAR
Software
- cQSAR. A regression program that has dual databases of over 21,000 QSAR models. Distributed by BioByte.
- SeeSAR. Program for interactive, visual compound promotion and optimization. It include PD and PK parameters and can be linked to other modules for physicochemical and ADME. Distributed by Bio
- clogP. Program for calculating log Poct/water from structure. Distributed by BioByte.
- ClogP/CMR. Estimates Molar Refractivity and logP. Distributed by Tripos.
Web services
- XScore-LogP. Calculates the octanol/water partition coefficient for a drug, based on a feature of the X-Score program.
ADME Toxicity
Software
- QikProp. Provides rapid ADME predictions of drug candidates. Distributed by Schrodinger.
- VolSurf. Calculate ADME Properties and Create Predictive ADME Models. Distributed by Tripos.
- GastroPlus. Simulates the oral absorption, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics for drugs in human and preclinical species. The underlying model is the Advanced Compartmental Absorption and Transit (ACAT) model. Distributed plu Simulation Plus, Inc.
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.
- ADMET Predictor. Software for advanced predictive modeling of ADMET properties. ADMET Predictor estimates a number of ADMET properties from molecular structures, and is also capable of building predictive models of new properties from user's data via its integrated ADMET Modeler module. Distributed by Simulations Plus, Inc.
- DDDPlus. Models and simulates the in vitro dissolution of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and formulation excipients dosed as powders, tablets, capsules, and swellable or non-swellable polymer matrices under various experimental conditions. Distributed by Simulations Plus, Inc.
- ADMEWORKS ModelBuilder. Builds QSAR/QSPR models that can later be used for predicting various chemical and biological properties of compounds. Models are based on values of physicochemical, topological, geometrical, and electronic properties derived from the molecular structure, and can be imported into ADMEWORKS Predictor.
- ADMEWORKS Predictor. QSAR based Virtual (in silico) screening system intended for simultaneous evaluation of the properties of compounds.
- MedChem Designer. Tool that combines molecule drawing features with a few free ADMET property predictions from ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulations Plus, Inc.
- IMPACT-F. Expert system to estimate oral bioavailability of drug-candidates in humans. IMPACT-F is composed of several QSAR models to predict oral bioavailability in humans. Developed by PharmaInformatic, Germany.
- MolScore-Drugs. Expert system to identify and prioritise drug candidates. Developed by PharmaInformatic, Germany.
- Natural product likeness calculator. Calculates Natural Product(NP)-likeness of a molecule, i.e. the similarity of the molecule to the structure space covered by known natural products. NP-likeness is a useful criterion to screen compound libraries and to design new lead compounds. Free and open source.
- ADMET Modeler. Integrated module of ADMET Predictor that automates the process of making high quality predictive structure-property models from sets of experimental data. It works seamlessly with ADMET Predictor structural descriptors as its inputs, and appends the selected final model back to ADMET Predictor as an additional predicted property. Distributed by Simulations Plus, Inc.
- Metabolizer. Enumerates all the possible metabolites of a given substrate, predicts the major metabolites and estimates metabolic stability. It can be used for the identification of metabolites by MS mass values, discovery of metabolically sensitive functionalities and toxicity prediction, and provide information related to the environmental effects of chemicals by bacterial degradation. Provided by ChemAxon.
- ACD/PhysChem Suite. Predicts basic physicochemical properties, like pKa, logP, logD, aqueous solubility and other molecular properties in seconds, usr a fragment-based models. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
- ACD/ADME Suite. Predicts of ADME properties from chemical structure, like Predict P-gp specificity, oral bioavailability, passive absorption, blood brain barrier permeation, distribution, P450 inhibitors, substrates and inhibitors, maximum recommended daily dose, Abraham-type (Absolv) solvation parameters. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
- ACD/Tox Suite. Collection of software modules that predict probabilities for basic toxicity endpoints. Several modules including hERG Inhibition, CYP3A4 Inhibition, Genotoxicity, Acute Toxicity, Aquatic Toxicity, Eye/Skin Irritation, Endocrine System Disruption, and Health Effects. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
- ACD/DMSO Solubility. Predicts solubility in DMSO solution. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
- Filter-it. Command-line program for filtering molecules with unwanted properties out of a set of molecules. The program comes with a number of pre-programmed molecular properties that can be used for filtering. Open source software distributed by Silicos.
- Virtual LogP. Bernard Testa's Virtual logP calculator. Provided by the Drug Design Laboratory of the University of Milano.
- FAF-Drugs2. Free package for in silico ADMET filtering. Distributed by the university of Paris Diderot.
- Discovery Studio TOPKAT Software. Cross-validated models for the assessments of chemical toxicity from chemical's molecular structure. Distributed by Accelrys.
- Discovery Studio ADMET Software. The ADMET Collection provides components that calculate predicted absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties for collections of molecules. Distributed by Accelrys.
- PreADME. Calculates molecular descriptors. Predicts Drug-likeness. ADME predictions.
- Molcode Toolbox. Molcode Toolbox allows prediction of medicinal and toxicological endpoints for a large variety of chemical structures, using proprietary QSAR models.
- KOWWIN - EPI Suite. Estimates the log octanol-water partition coefficient of chemicals using an atom/fragment contribution method. Distributed by the EPA~s Office of Pollution Prevention Toxics and Syracuse Research Corporation (SRC) as part of the EPI Suite. For Windows.
- ADRIANA.Code. Program to calculate physico-chemical properties of small molecules: number of H-bonds donor and acceptors, logP, logS, TPSA, dipole moment, polarizability, etc. Distributed by Molecular Networks.
- Derek Nexus. Predicts toxicity properties using QSAR and other expert knowledge rules. Distributed by Lhasa Limited.
- Meteor. Predicts metabolic fate of chemicals using other expert knowledge rules in metabloism. Distributed by Lhasa Limited.
- OncoLogic. Evaluates the likelihood that a chemical may cause cancer, using SAR analysis, experts decision mimicking and knowledge of how chemicals cause cancer in animals and humans. Distributed for free by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- HazardExpert Pro. Predicts the toxicity of organic compounds based on toxic fragments. Distributed by CompuDrug.
- MetabolExpert. Predicts the most common metabolic pathways in animals, plants or through photodegradation. Distributed by CompuDrug.
- MEXAlert. Identifies compounds that have a high probability of being eliminated from the body in a first pass through the liver and kidney. Distributed by CompuDrug.
- PrologP/PrologD. Predicts the logP/logD values using a combination of linear and neural network methods. Distributed by CompuDrug.
- pKalc. Program for predicting acidic and basic pKa. Distributed by CompuDrug.
- Leadscope. Estimates toxiticy using QSAR. Distributed by Leadscope.
- COMPACT. Identifies potential carcinogenicity or toxicities mediated by CYP450s.
- CASETOX. Uses MCASE to predict toxicity. Distributed by MultiCASE.
- META. Predicts metabolic paths of molecules. Distributed by MultiCASE.
- PK-Sim. Predicts ADMET properties. Distributed by Bayer technology Services.
- SimCYP. The SimCYP Population-based ADME Simulator is a platform for the prediction of drug-drug interactions and pharmacokinetic outcomes in clinical populations. Distributed by SimCYP.
- SimCYP for iPhone.. The SimCYP Population-based ADME Simulator is a platform for the prediction of drug-drug interactions and pharmacokinetic outcomes in clinical populations. For iPhone. Distributed by SimCYP.
- Cloe Predict. Pharmacokinetic prediction using phisiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling (PBPK), and prediction of human intestinal absorption using solubility, pKa and Caco-2 permeability data. Distributed by Cyprotex Discovery.
- KnowItAll - ADME | Tox Edition. Prediction of ADME Tox properties using consensus modeling. Distributed by Bio-Rad Laboratories.
- PASS. Identification of probable targets and mechanisms of toxicity.
- MetaDrug. Predicts toxicity and metabolism of compounds using >70 QSAR models for ADME/Tox properties. Distributed by Thomson ReutersLC.
- MetaSite. Computational procedure that predicts metabolic transformations related to cytochrome-mediated reactions in phase I metabolism. The method predicts "hot spots" in the molecule, suggests the regions that contribute most towards each "hot spot", providing additional derivation sites for chemists to design new stable compounds, predicts the structures of the most likely metabolites and warns about the potential of CYP mechanism-based inhibition. Distributed by Moldiscovery.
- IMPACTS. In-silico Metabolism Prediction by A ctivated Cytochromes and Transition States (IMPACTS) predicts site of metabolism on small molecules by CYP450. This program combines docking to metabolic enzymes, transition state modeling, and rule-based substrate reactivity prediction. It is included in the Forecaser suite and provided by Molecular Forecaster Inc.
- FAME2. Program to predict site of metabolism and regioselectivity of CYP450 oxidation. Machine learnin approach relying on randomized trees and simple 2D descriptors. Software package free of charge from the Department of Computer Science, Center for Bioinformatics, Universität Hamburg, Germany.
- StarDrop. Allows the identification of the region of a molecule that are the most vulnerable to metabolism by the major drug metabolising isoforms of cytochrome P450. Distributed by optibrium.
- isoCYP. Software for the prediction of the predominant human cytochrome P450 isoform by which a given chemical compound is metabolized in phase I. Distributed by Molecular Networks.
Web services
- ALOGPS. On-line prediction of logP, water solubility and pKa(s) of compounds for drug design (ADME/T and HTS) and environmental chemistry studies. ALOGPS also displays values calculated with Pharma Algorithms LogP, LogS and pKa, Actelion LogP & LogS (many thanks to Dr Thomas Sander), Molinspiration logP, KOWWIN logP, ALOGP (Viswanadhan et al, 1989), MLOGP (Moriguchi et al, 1992) implemented in the DragonX software, XLOGP2 and XLOGP3 programs and ChemAxon logP calculator
- OSIRIS Property Explorer. Integral part of Actelion's inhouse substance registration system. Calculates on-the-fly various drug-relevant properties for drawn chemical structures, including some toxicity and druglikeness properties. Maintained by the Virtual Computational Chemistry Laboratory.
- SwissADME. A web tool that gives access to a pool of fast yet robust predictive models for physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, druglikeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness, among which in-house proficient methods such as the BOILED-Egg, iLOGP, Bioavailability radar and Synthetic Accessibility score. Easy efficient input and interpretation are ensured thanks to the user-friendly interface through a login-free website. Sepcialists, but also nonexperts in chemoinformatics and computational chemistry can predict rapidly key parameters for a collecion of molecules to support their medicinal chemistry endeavors. Developed and maintained by the Molecular Modeling Group of the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics.
- Chemicalize. Calculates or predict molecular properties, including logP, tautomers, PSA, pK, lipinski-like filters, etc. Provided by ChemAxon.
- AquaSol. Predicts aqueous solubility of small molecules using UG-RNN ensembles. Provided by the University of california, Irvine.
- Molinfo. Calculates or predict molecular properties other than 3D structure. Provided by the University of california, Irvine.
- ToxCreate. Web service to create computational models to predict toxicity. Provided by OpenTox.
- ADME-Tox. ADME-Tox (poor absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination (ADME) or toxicity) filtering for small compounds, based on a set of elementary rules.
- ToxPredict. Web service to estimate toxicological hazard of a chemical structure. Molecules can be drawn, or input by any identifier (CAS, Name, EINECS) or SMILES or InChI or URL of OpenTox compound or dataset. Provided by OpenTox.
- ToxiPred. A server for prediction of aqueous toxicity of small chemical molecules in T. pyriformis. User can submit chemical molecules in the commonly used format (mol/SMILE/sdf) and after descriptors calculation the server will predict the pIGC50 value of the molecule.
- DrugMint. Web server predicting the drug-likeness of compounds.
- STITCH. Resource to explore known and predicted interactions of chemicals and proteins. Chemicals are linked to other chemicals and proteins by evidence derived from experiments, databases and the literature. STITCH contains interactions for over 74,000 small molecules and over 2.5 million proteins in 630 organisms.
- PPS. (UM-BBD Pathway Prediction System). Webservice to predict plausible pathways for microbial degradation of chemical compounds. Predictions use biotransformation rules, based on reactions found in the UM-BBD database or in the scientific literature. A list of all rules is available. Maintained by the University of Minnesota.
- DrugLogit. Web service to predict the probability of a compound being classified as a drug or non-drug, as well as disease category (or organ) classification (DC). Maintained by the Institute of Chemistry, University of Tartu, Estonia.
- XScore-LogP. Calculates the octanol/water partition coefficient for a drug, based on a feature of the X-Score program.
- VirtualToxLab. ''In silico'' tool for predicting the toxic (endocrine-disrupting) potential of existing and hypothetical compounds (drugs, chemicals, natural products) by simulating and quantifying their interactions towards a series of proteins known to trigger adverse effects using automated, flexible docking combined with multi-dimensional QSAR (mQSAR).
- pkCSM. A novel approach to the prediction of pharmacokinetic properties, which relies on graph-based signatures. These encode distance patterns between atoms and are used to represent the small molecule and to train predictive models. They were successfully used across five main different pharmacokinetic properties classes to develop predictive regression and classification models. A web server to provide an integrated freely available platform to rapidly screen multiple pharmacokinetic properties was developed by the University of Cambridge, UK.
- admetSAR. admetSAR provides the manually curated data for diverse chemicals associated with known Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Toxicity profiles. admetSAR allows searching for ADMET properties profiling by name, CASRN and similarity search. In addition, admetSAR can predict about 50 ADMET endpoints by our recently development chemoinformatics-based toolbox, entitled ADMET-Simulator.
- Pred-Skin. Pred-Skin is based on statistically significant and externally predictive QSAR models of skin sensitization. The models were built using a large database containing human and murine local lymph node assay data. Developed and provided freely for diverse plateforms by the Laboratory for Molecular Modeling and Drug Design, Federal University of Goiás, Brazil.
- Pred-hERG. Pred-hERG is based on statistically significant and externally predictive QSAR models. The models were built using 16,932 entry in ChEMBL associated with bioactivity on hERG. Developed and provided freely for diverse plateforms by the Laboratory for Molecular Modeling and Drug Design, Federal University of Goiás, Brazil.
- PharmMapper. Freely accessed web-server designed to identify potential target candidates for the given probe small molecules (drugs, natural products, or other newly discovered compounds with binding targets unidentified) using pharmacophore mapping approach.
- MODEL - Molecular Descriptor Lab. Computes structural and physichemical properties of molecules from their 3D structures. Maintained by the University of Singapore.
- PreADMET. Web-based application for predicting ADME data and building drug-like library using in silico method.
- Free ADME Tools. ADME Prediction Toolbox of the SimCYP application provided free of charge by SimCYP.
- Lazar. Lazy Structure Activity Relationships. Derives predictions from toxicity databases by searching for similar compounds. provided free of charge by in silico toxicology.
- UM-BBD Pathway Prediction System. The PPS predicts plausible pathways for microbial degradation of chemical compounds. Predictions use biotransformation rules, based on reactions found in the UM-BBD database or in the scientific literature. Provided by the University of Minnesota.
- MetaPrint2D. Metabolic site predictor. MetaPrint2D is a tool that predicts xenobiotic metabolism through data-mining and statistical analysis of known metabolic transformations reported in scientific literature. MetaPrint2D-React can make predictions concerning a wider range of reactions than MetaPrint2D, and is able to predict the types of transformation that can take place at each site of metabolism, and the likely metabolite formed. Provided by the University of Cambridge.
- RA. Way2drug RA is a web-service for in silico prediction of reacting atoms. Prediction of sites of transformation for drug-like compounds for nine classes of metabolic reactions. Provided by the Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, Moscow, Russia
- MetaPrint2D-React.. Metabolic site predictor. MetaPrint2D is a tool that predicts xenobiotic metabolism through data-mining and statistical analysis of known metabolic transformations reported in scientific literature. MetaPrint2D, which predicts sites of phase I metabolism, defined as the addition of oxygen (e.g. hydroxylation, oxidation, epoxidation) or elimination reactions. Provided by the University of Cambridge.
- MetaTox. MetaTox uses a collection of biotransformation reactions and QSAR models to predict the structure, probability and toxicity of metabolites for a given input molecules. Provided as a free web service by the Institute of Biomedical Chemistry (IBMC), Moscow, Russia.
- MetaPred. MetaPred Server predict metabolizing CYP isoform of a drug molecule/substrate, based on SVM models developed using CDK descriptors.
- Property calculator. Create a physicochemical property profile for a compound. Provided by mcule.
- Aggregator Advisor. Free web service to suggest molecules that aggregate or may aggregate under biochemical assay conditions. The approach is based on the chemical similarity to known aggregators, and physical properties. Provided by the Shoichet Laboratory in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
- Toxicity checker. Webserver for searching substructures commonly found in toxic and promiscuous ligands. Based on more than 100 SMARTS toxic matching rules. Provided by mcule.
Databases
- PACT-F. (Preclinical And Clinical Trials Knowledge Base on Bioavailability). Preclinical And Clinical Trials Knowledge Base on Bioavailability (PACT-F). The database contains 8296 records, which describe in detail the results of clinical trials in humans and preclinical trials in animals. PACT-F is extensively annotated. Up to 17 fields describe in detail the results and conditions of each trial, such as route of administration, species investigated, drug formulation, coadministration of drug, feeding condition, age and gender of the subjects involved, dosing scheme, genetic differences, experimental and analytical procedure, method of calculation and state of health. Provided by PharmaInformatic, Germany.
- TOXNET. Databases on toxicology, hazardous chemicals, environmental health, and toxic releases that can be accessed using a common search interface. provided by the Unied States NLM.
- Leadscope Toxicity Database. Database of 160,000 chemical structures with toxicity data. Distributed by Leadscope.
- WOMBAT-PK. Database for Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Drug Target Information. WOMBAT-PK contains 1260 entries (1260 unique SMILES), totaling over 9,450 clinical pharmacokinetic measurements; it further includes 2,316 physico-chemical properties; 932 toxicity endpoints, and 2,186 annotated drug-target bioactivities. Compiled by Sunset Molecular Discovery LLC.
- Cloe Knowledge. Open Access ADME/PK Database for a range of marketed drugs. Maintained by Cyprotex.
- PHYSPROP. The Physical Properties Database (PHYSPROP) contains chemical structures, names, and physical properties for over 41,000 chemicals. Physical properties are collected from a wide variety of sources, and include experimental, extrapolated, and estimated values for melting point, boiling point, water solubility, octanol-water partition coefficient, vapor pressure, pKa, Henry's Law Constant, and OH rate constant in the atmosphere. Maintained by SRC.
- SIDER. Contains information on marketed medicines and their recorded adverse drug reactions. The information is extracted from public documents and package inserts. The available information include side effect frequency, drug and side effect classifications as well as links to further information, for example drug–target relations. Provided by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany.
- admetSAR. admetSAR provides the manually curated data for diverse chemicals associated with known Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Toxicity profiles. admetSAR allows searching for ADMET properties profiling by name, CASRN and similarity search. In addition, admetSAR can predict about 50 ADMET endpoints by our recently development chemoinformatics-based toolbox, entitled ADMET-Simulator.
- The ADME databases. Databases for benchmarking the results of experiments, validating the accuracy of existing ADME predictive models, and building new predictive models.
- The ADME database. Provides comprehensive data for structurally diverse compounds associated with known ADME properties, including human oral bioavailability, enzymes metabolism, inhibition and induction, transport, plasma protein binding and bloodbrain barrier. Distributed by Aureus.
- UCSF-FDA Transportal. The purpose of this database is to be a useful repository of information on transporters important in the drug discovery process as a part of the US Food and Drug Administration-led Critical Path Initiative. Information includes transporter expression, localization, substrates, inhibitors, and drug-drug interactions It contains 3438 compounds, 11649 interaction records, 1211 literature references. The FDA has partnered with the Giacomini lab at UCSF to create a transporter database of pharmacologically relevant transporters to support development of new pharmaceuticals. Information on important transporters, their localization, expression levels, substrates, and inhibitors have been curated from the literature and compiled into a single location to aid and inform drug developers, regulatory agencies and academic scientists about transporters important in drug action and disposition.. The database will also help drug developers in determining what experiments or analyses must be conducted to check for possible drug interactions through transporters as well as identify promising transporter candidates for the testing of possible genetic influences.
- SuperTarget Database. Database of about 332828 drug-target relations.
- DART. (Drug Adverse Reaction Target). A database for facilitating the search for drug adverse reaction target. It contains information about known drug adverse rection targets, functions and properties. Associated references are also included. Maintained by the University of Singapore.
- DITOP. (Drug-Induced Toxicity Related Proteins). Database of proteins that mediate toxicities through their interaction with drugs or reactive metabolites. Can be searched using keywords of chemicals, proteins, or toxicity terms. Maintained by the Xiamen university.
- ADMEAP. A database for facilitating the search for drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion associated proteins. It contains information about known drug ADME associated proteins, functions, similarities, substrates / ligands, tissue distributions, and other properties of the targets. Associated references are also included. Currently this database contains 321 protein entries. Maintained by the Dept.Computational Science. NUS.
- SIDER. (Side Effect Resource). contains information on marketed medicines and their recorded adverse drug reactions. The information is extracted from public documents and package inserts. The available information include side effect frequency, drug and side effect classifications as well as links to further information, for example drug–target relations.
- SAR Genetox Database. Genetic toxicity database to be used as a resource for developing predictive modeling training sets. Distributed by Leadscope.
- SAR Carcinogenicity Database. Carcinogenicity database with validated structures to be used as a resource for preparing training sets. Distributed by Leadscope.
- HMDB. The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. The database contains chemical data, clinical data, and molecular biology/biochemistry data. The database (version 2.5) contains over 7900 metabolite entries including both water-soluble and lipid soluble metabolites as well as metabolites that would be regarded as either abundant (> 1 uM) or relatively rare (< 1 nM). Provided by the Departments of Computing Science & Biological Sciences, University of Alberta.
- t3db. (Toxin and Toxin Target Database). Combines detailed toxin data with comprehensive toxin target information. The database currently houses over 2900 toxins described by over 34 200 synonyms, including pollutants, pesticides, drugs, and food toxins, which are linked to over 1300 corresponding toxin target records. Altogether there are over 33 800 toxin, toxin target associations. Each toxin record (ToxCard) contains over 50 data fields and holds information such as chemical properties and descriptors, toxicity values, molecular and cellular interactions, and medical information. This information has been extracted from over 5600 sources, which include other databases, government documents, books, and scientific literature. Provided by the Departments of Computing Science & Biological Sciences, University of Alberta.
- SuperToxic. Collection of toxic compounds from literature and web sources. The current version of this database compiles approx. 60,000 compounds with about 100,000 synonyms. These molecules are classified according to their toxicity based on more than 2,500,000 measurements. Provided by Charité Berlin, Structural Bioinformatics Group.
- SuperHapten. Comprehensive database for small immunogenic compounds. Contains currently 7257 haptens, 453 commercially available related antibodies and 24 carriers. Provided by Charité Berlin, Institute of Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics.
- HaptenDB. Database of about 1087 haptens that includes common and chemical name of Hapten, molecular mass, physical and chemical properties, biological importance and the structure. Provided by the Institute of Microbial Technology, India.
- SuperCyp. Comprehensive database on Cytochrome P450 enzymes including a tool for analysis of CYP-drug interactions. Provided by Charité Berlin, Structural Bioinformatics Group.
- PROMISCUOUS. Exhaustive resource of protein-protein and drug-protein interactions with the aim of providing a uniform data set for drug repositioning and further analysis. PROMISCUOUS contains three different types of entities: drugs, proteins and side-effects as well as relations between them. Provided by Charité Berlin, Structural Bioinformatics Group.